In the absence of an appropriate amount of "good microorganisms", especially organic fertilizers processed at high temperatures and short periods of time, once the organic fertilizer made from organic waste is applied to the soil, not only has hidden risks for growth of crops, but also has health concerns for human consumption in the future.
We add "beneficial composting microorganisms" to the food waste processed by high temperature and high pressure processing for research.
The test results show that the compost can be harmless after 3 days! The number of probiotics is as high as 1 billion (10 to the 9th power) CFU/g(Note3)!
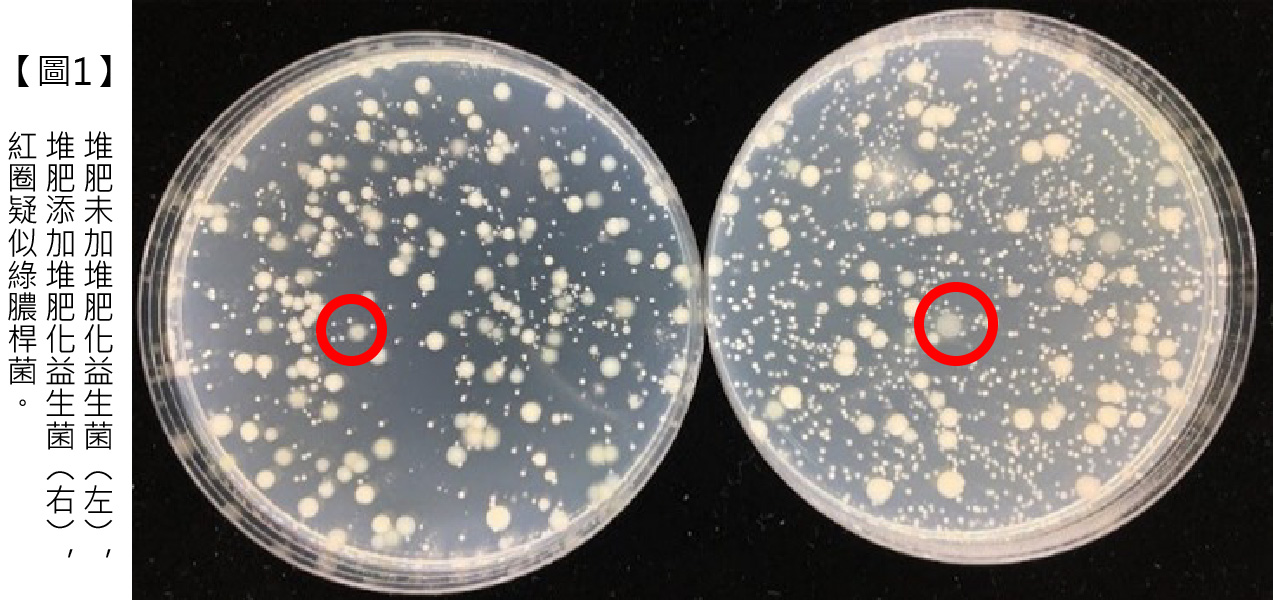
Surprisingly, the control group without probiotics is most likely to be polluted by the environment. It consists of Pseudomonas aeruginosa(Note1)as a accounts for 20% of the total number of live bacteria(Picture1/Left), while the consists of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the experimental group treated with probiotics is only accounted for 0.05%.The test results successfully confirmed the effectiveness of probiotics!
Recently, SH Agricultural Biotechnology accepted a commission from a factory for mushroom waste disposal. When SH team arrived at the scene, they picked up the discarded mushroom bags that had not been added with probiotics and observed carefully. They found that the discarded mushroom bags were covered with a large number of fungi in just 1 to 2 days, which even interwoven into a cushion-like structure(Picture2/Right). These fungi not only blocked the exchange of air, but also seriously affected composting.。
This is the reason why SH Agricultural Biotechnology is based on scientific theories and screened out "beneficial microorganisms" that have the functions of deodorizing, promoting composting, inhibiting pathogenic bacteria and insecticidal eggs, promoting plant growth and assisting plants in dissolving difficult-to-decompose nutrients in the soil for plant absorption. [END]
-
♦Note1、The Ministry of Health and Welfare in Taiwan and other countries in the world classify microbial safety into the following four groups:
.
1. Risk Group 1(RG1): Not affect human health.
2. Risk Group 2(RG2): Diseases caused by humans are rarely serious, and there are usually methods of prevention and treatment. (E.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, dengue fever and Enterovirus)
3. Risk Group 3(RG3): The dangerous group of microorganisms can cause serious or fatal human diseases, and there may have methods of prevention and treatment. (E.g. coronavirus, bird flu)
4. Risk Group 4(RG4): The dangerous group of microorganisms can cause serious or fatal diseases in humans, and there is usually no method of prevention and treatment. (E.g. Ebola, smallpox)
-
♦Note 2、Information of Pseudomonas aeruginosa / Data source: LaBauve, A.E., and M.J. Wargo. 2012. LaBauve, A.E., and M.J. Wargo. 2012. Growth and Laboratory Maintenance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a general, non-parasitic, Gram-negative bacteria. It is an opportunistic pathogen that may cause major diseases. Its characteristics of fast growth, facile genetics and virulence-related phenotypes make it a common model organism for studying Gram-negative opportunistic pathogens and basic microbiology.
.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a unique Gram-negative bacteria. It has a wide range of metabolic diversity, enabling it to multiply in a very wide range of environments and nutrient sources. Its large metabolic flexibility is part of the reason why it can become an opportunistic pathogen. Pseudomonas aeruginosa often causes community-acquired infections and hospital-acquired infections, and its impact ranges from cosmetic to life-threating.
.
Symptoms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections include ulcerative keratitis of the eyes, skin and soft tissue folliculitis, which are common symptoms of wounds in diabetic patients, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa may cause more serious diseases to people with weakened immune functions. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is also a common cause of nosocomial infections, and its symptoms include burns, scalds, urinary tract infections, bacteremia, and pneumonia (Sadikot et al., 2005). Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections account for 11-13.8% of all hospital-acquired infections (Driscoll et al., 2007). In addition, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is the main pathogen causing disease and death in most cystic fibrosis (CF) patients with recessive genetic disorder cystic fibrosis (Burns et al., 1998).
-
♦Note3、CFU(colony-forming unit):CFU/g"the number of viable bacteria per gram of sample.。